1、JDBC 取得数据库自动生成的主键
获取自增长的键值:
(1)在创建PreparedStatement对象时
原来:
PreparedStatement pst = conn.preparedStatement(sql);
现在:
PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement(orderInsert,Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
(2)原来执行更新
原来:
int len = pst.executeUpdate();
现在:
int len = pst.executeUpdate();
ResultSet rs = pst.getGeneratedKeys();
if(rs.next()){
Object key = rs.getObject(第几列);//获取自增长的键值
}
|
package com.atguigu.other;
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.Statement; import java.util.Scanner;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.atguigu.utils.JDBCUtils;
public class TestGetGenericKey { @Test public void add() throws Exception { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println(“请输入姓名:”); String name = input.nextLine();
System.out.println(“请输入性别:”); String gender = input.nextLine();
System.out.println(“请输入领导编号:”); int mid = input.nextInt();
System.out.println(“请输入部门编号:”); int did = input.nextInt();
String sql = “INSERT INTO emp VALUES(NULL,?,?,?,?)”;// 参数,占位符,通配符,表示这个地方需要设置值
// 2、获取连接 Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
// 3、准备一个PreparedStatement:预编译sql // 执行添加语句,如果需要获取自增长的键值,那么在此处要告知mysql服务器,在创建PreparedStatement对象时,增加一个参数 //autoGeneratedKeys – 指示是否应该返回自动生成的键的标志,它是 Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS 或 Statement.NO_GENERATED_KEYS 之一 PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement(sql,Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
// 4、把?用具体的值进行代替 pst.setString(1, name); pst.setString(2, gender); pst.setInt(3, mid); pst.setInt(4, did);
// 5、执行sql int len = pst.executeUpdate();
ResultSet rs = pst.getGeneratedKeys(); if(rs.next()){ System.out.println(“新员工编号是:” + rs.getObject(1)); }
// 6、释放资源 JDBCUtils.closeQuietly(pst, conn); } }
|
2、批处理
当需要成批插入或者更新记录时。可以采用Java的批量更新机制,这一机制允许多条语句一次性提交给数据库批量处理。通常情况下比单独提交处理更有效率。
JDBC的批量处理语句包括下面两个方法:
- addBatch():添加需要批量处理的SQL语句或参数
- executeBatch():执行批量处理语句;
通常我们会遇到两种批量执行SQL语句的情况:
- 多条SQL语句的批量处理;
- 一个SQL语句的批量传参;
注意:
JDBC连接MySQL时,如果要使用批处理功能,请再url中加参数?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
PreparedStatement作批处理插入时使用values(使用value没有效果)
2.1 Statement
void addBatch(String sql):添加需要批量处理的SQL语句
int[] executeBatch();执行批量处理语句;
2.2 PreparedStatement
void addBatch()将一组参数添加到此 PreparedStatement 对象的批处理命令中
int[] executeBatch();执行批量处理语句;
2.3 关于效率测试
测试:插入100000条记录
- (1)Statement不使用批处理
- (2)PreparedStatement不使用批处理
- (3)Statement使用批处理
- (4)PreparedStatement使用批处理(效率最高)
- >(3)>(1)>(2)
2.4 示例代码
|
package com.atguigu.other;
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.atguigu.utils.JDBCUtils;
public class TestBatch { /* * 没有使用批处理 */ @Test public void testNoBatch() throws Exception { long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//批处理 //添加500件商品 String sql = “INSERT INTO t_goods (pname,price) VALUES(?,?)”;
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { String pname = “商品” + i; double price = i;
pst.setString(1, pname); pst.setDouble(2, price);
int len = pst.executeUpdate(); System.out.println(“第” +i +”条添加:” + (len>0?”成功”:”失败”)); }
long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(“耗时:” + (end-start)); }
@Test public void testBatch()throws Exception { long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String sql = “INSERT INTO t_goods (pname,price) VALUES(?,?)”;
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { String pname = “商品” + i; double price = i; pst.setObject(1, pname); pst.setObject(2, price);
pst.addBatch();//添加到批处理中 }
int[] executeBatch = pst.executeBatch();//一批命名同时执行 for (int i = 0; i < executeBatch.length; i++) { System.out.println(“第” +i +”条添加:” + (executeBatch[i]>0?”成功”:”失败”)); }
JDBCUtils.closeQuietly(pst, conn);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(“耗时:” + (end-start));
} }
|
3、事务
JDBC程序中当一个连接对象被创建时,默认情况下是自动提交事务:每次执行一个 SQL 语句时,如果执行成功,就会向数据库自动提交,而不能回滚。
JDBC程序中为了让多个 SQL 语句作为一个事务执行:(重点)
- 调用 Connection 对象的 setAutoCommit(false); 以取消自动提交事务
- 在所有的 SQL 语句都成功执行后,调用 commit(); 方法提交事务
- 在其中某个操作失败或出现异常时,调用 rollback(); 方法回滚事务
- 若此时 Connection 没有被关闭, 则需要恢复其自动提交状态 setAutoCommit(true);
注意:
如果多个操作,每个操作使用的是自己单独的连接,则无法保证事务。即同一个事务的多个操作必须在同一个连接下
JDBC还可以通过Connection对象的:
- int getTransactionIsolation():获取此 Connection 对象的当前事务隔离级别
- void setTransactionIsolation(int level):试图将此 Connection 对象的事务隔离级别更改为给定的级别。可能的事务隔离级别是 Connection 接口中定义的常量。
level – 以下 Connection 常量之一:
- TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED(=1)
- TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED(=2)、
- TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ(=4)
- TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE(=8)。
(注意,不能使用 Connection.TRANSACTION_NONE(=0),因为它指定了不受支持的事务。)
 |
|
package com.atguigu.other;
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.atguigu.utils.DBUtils;
public class TestTransaction {
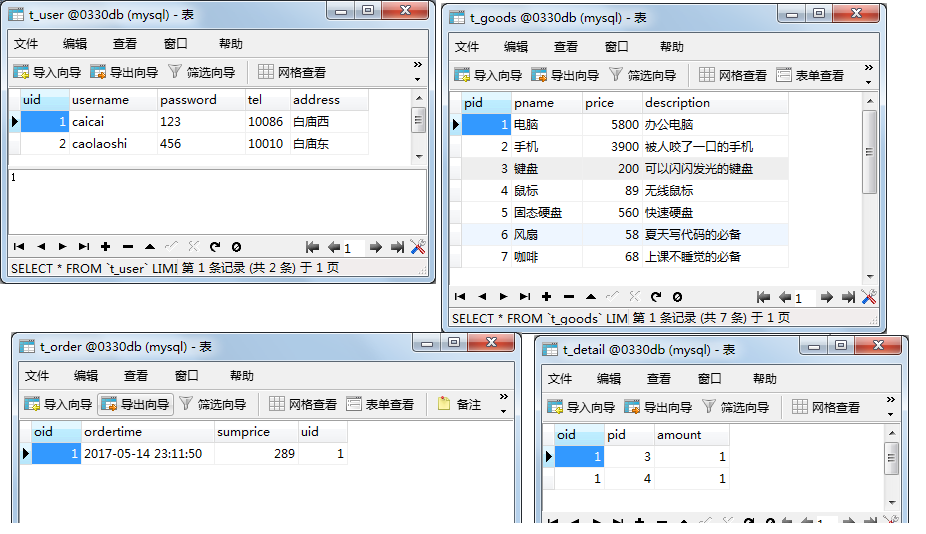
@Test public void test() { int uid = 2;//谁买的 int[] pids = {1,2,3};//购买的商品的编号 int[] amount = {1,1,1};//分别每一个商品的数量 double[] price = {45,34,2.5};//购买时,每一件商品的价格
//如何把这些订单的数据保存到数据库中 //分别在订单表t_order添加一条记录:订单编号,订单时间,订单总价,用户编号 //在订单明细表t_detail添加几条记录:订单编号,商品编号,数量(多行),这里3行
//这些数据要么同时保存成功,要么同时失败(撤销),那么表示他们要组成一个事务
Connection conn = null; try {
//手动提交事务 //1、获取连接对象(注册驱动省略,因为在DBUtils注册过了) conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); //2、设置手动提交 conn.setAutoCommit(false);
String orderInsert = “INSERT INTO t_order (sumprice,uid) VALUES(?,?)”; double sumprice = 0; for (int i = 0; i < price.length; i++) { sumprice += price[i]*amount[i]; } //3、执行添加语句,如果需要获取自增长的键值,那么在此处要告知mysql服务器,在创建PreparedStatement对象时,增加一个参数 //autoGeneratedKeys – 指示是否应该返回自动生成的键的标志,它是 Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS 或 Statement.NO_GENERATED_KEYS 之一 PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement(orderInsert,Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
pst.setObject(1, sumprice); pst.setObject(2, uid); pst.executeUpdate();
ResultSet rs = pst.getGeneratedKeys(); if(rs.next()){ Object oid = rs.getObject(1);
String detailInsert = “INSERT INTO t_details (oid,pid,amount) VALUES(?,?,?)”; PreparedStatement pst2 = conn.prepareStatement(detailInsert); for (int i = 0; i < pids.length; i++) { pst2.setObject(1, oid); pst2.setObject(2, pids[i]); pst2.setObject(3, amount[i]);
pst2.addBatch(); }
pst2.executeBatch(); }
//4、提交事务 conn.commit(); System.out.println(“添加成功”); }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); try { //如果发生异常,应该回滚 if(conn!=null){ System.out.println(“添加失败”); conn.rollback(); } } catch (SQLException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } }finally{ try { //释放资源 if(conn!=null){ conn.setAutoCommit(true); conn.close(); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
|
上一篇: 感觉自己比较笨,学大数据可以吗
下一篇: Java培训课程之数据库的操作或访问

